LM101-046: How to Optimize Student Learning using Recurrent Neural Networks (Educational Technology)
Podcast: Play in new window | Download | Embed
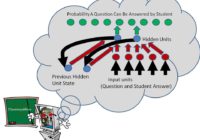
LM101-046: How to Optimize Student Learning using Recurrent Neural Networks (Educational Technology) Episode Summary: In this episode, we briefly review Item Response Theory and Bayesian Network Theory methods for the assessment and optimization of student learning and then describe a poster presented on the first day of the Neural Information Processing Systems conference in December 2015 in Montreal… Read More »